Exploring ourselves and the “others”
Exploring ourselves and the “others”
This module examines the perceptions of ourselves and the ways that we see “others” and others see us, focusing on the role of stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination.
This module offers you:

INTRODUCTION
Aim & Learning Outcomes
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
Key concepts, background information, relevant theories
ACTIVITIES
Exercises, self-reflection & practical resources to promote inclusive e-learning
USEFUL TIPS
Advice, ideas and proposals on relevant issues
USEFUL READING
References and further reading
Aim
A module examining the perceptions of ourselves and the ways that we see “others” and others see us, focusing on the role of stereotypes, prejudice and discrimination.
A module examining the perceptions of ourselves and the ways that we see “others” and others see us, focusing on the role of stereotypes, prejudice and discrimination.
Learning objectives
After the completion of this module, learners (VET teachers/trainers/educators and also VET providers/Staff, as well as other key actors of educational sector) will be able to:
- Explain and self-reflect on how our societies depend on the way we define “ourselves” and “others”
- Understand the reasons behind people having negative attitudes and behaviours towards “others”
- Demonstrate awareness on protection against various forms of discrimination
At the end of this module you will know how to…
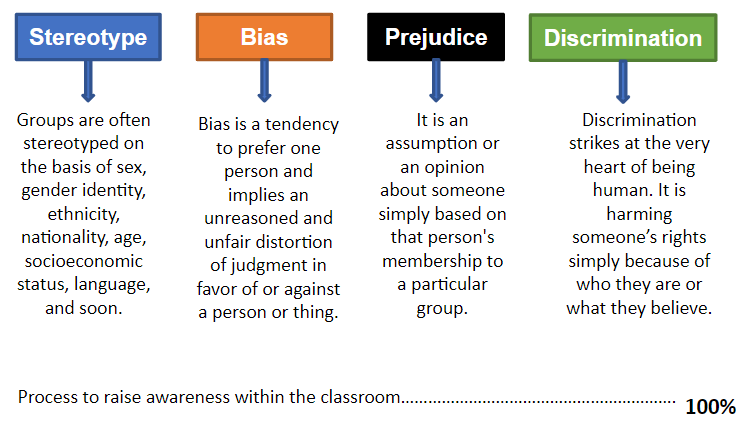
- Define the concepts of “self” and “identity”
- Clarify the terms stereotype, bias, prejudice and discrimination
- Summarize the EU anti-discrimination and human rights protection legal framework
- Identify forms of discrimination and relate them to personal experience
- Distinguish between different types of discrimination and their root (direct, indirect, structural applied to sexism, xenophobia, intolerance and racism)
- Examine some of discrimination’s specific manifestations, such as multiple discrimination, harassment or instruction to discriminate, victimisation, hate crime and hate speech
- Critically evaluate their own personal beliefs, attitudes and biases
- Apply effective strategies and techniques to avoid the “traps” of stereotyping, prejudice and discrimination
- Apply their knowledge of protection against discrimination on grounds of racial or ethnic origin, religion or belief, disability, age, gender or sexual orientation within their own life
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND

This modules demonstrates the benefits of three different units:
- The influences of stereotypes, bias, prejudice and discrimination
- Balancing the “self” and “identity” to build a transparent classroom and community
- The EU anti-discrimination and human rights protection legal framework
Unit 3.1: The influences of stereotypes, bias, prejudice and discrimination
Discrimination against non-nationals, is sometimes known as xenophobia…
Xenophobia often overlaps with forms of prejudice, including racism, but there are important distinctions. Where racism, and other forms of discrimination are based on specific characteristics, xenophobia is usually rooted in the perception that members of the outgroup are foreign to the ingroup community. Xenophobia does not just affect people at the individual level. It affects entire schools and societies.
Unit 3.1: The influences of stereotypes, bias, prejudice and discrimination
- Social and school insecurity
- Lack of contact with school staff/students from other cultures or backgrounds
- Fear of strangers and/or newcomers
- Inappropriate jokes
- Unfair performance reviews
- Hostile communication
- Isolation and controversial discussions

Unit 3.1: The influences of stereotypes, bias, prejudice and discrimination

Types of unconscious biases within schools and society
- Perception bias (it occurs when we judge others based on often inaccurate, stereotypes and assumptions about the group they belong in)
- Gender bias (the favoring of one gender over another)
- Ageism (it refers to stereotyping or discriminating against others based on their age)
- Confirmation bias (it is the tendency to seek out and use information that confirms one’s views)
- Affinity bias (the tendency to favor people who share similar interests, backgrounds, and experiences)
- Overconfidence bias (it is the tendency for people to think they are better at certain abilities and skills than they actually are)
- Anchor bias (it occurs when we overly rely on the first piece of information we receive as an anchor to base our decision-making upon)
- Unconscious bias, also known as implicit bias, is a learned assumption, belief, or attitude that exists in the subconscious, and we are not necessarily aware of.
Unit 3.2: Balancing the “self” and “identity” to build a transparent classroom and community
Do you see yourself how you really are or how others want you to be? In the school settings but also in the wider community people see themselves differently from how they see others. In personality psychology, the ‘’self’’ can be defined as the individual as a whole including all characteristics, attributes, mentality, and consciousness.
We are constantly thinking about what image to give others, about how they are going to view us.
‘’Identity’’ is largely concerned with the question: “Who are you?” What does it mean to be who you are? Identity relates to our basic values that dictate the choices we make (e.g., relationships, career).
Unit 3.2: Balancing the “self” and “identity” to build a transparent classroom and community
Even if we are at school or in society (in general) sometimes we make a mistake by starting with how we see things (“our here”). To help the other person move, we need to start with how they see things (“their there”).
Exploring the others in an effective way but in relation to ourselves we need to go from ‘’our here’’ to ‘’their there’’ to engage others in three specific ways:
1
Situational Awareness: Show that You Get “It.” (Show that you understand the opportunities and challenges your conversational ‘’colleague’’ is facing.)
2
Personal Awareness: You Get “Them.”(Show that you understand his or her strengths, weaknesses, goals, hopes, priorities, needs, limitations, fears, and concerns.)
3
Solution Awareness: You Get Their Path to Progress. (Show people a positive path that enables them to make progress on their own terms.)
Unit 3.3: The EU anti-discrimination and human rights protection legal framework
‘’Any discrimination based on any ground such as sex, race, colour, ethnic or social origin, genetic features, language, religion or belief, political or any other opinion, membership of a national minority, property, birth, disability, age or sexual orientation shall be prohibited.’’
The European Union (EU) believes that the promotion and protection of human rights around the world is a legitimate concern of the international community. The first significant step towards non-discrimination legislation was taken in 1997, when the European Union governments unanimously agreed to introduce a new article, now known as Article 13 into the EU Treaties. This Article now serves as a legal basis of all European non-discrimination legislation.
Human rights are at the heart of EU relations with other countries and regions. EU policy includes:
- Promoting the rights of women, children, minorities and displaced persons
- Opposing the death penalty, torture, human trafficking and discrimination
- Defending civil, political, economic, social and cultural rights
- Defending human rights through active partnership with partner countries, international and regional organisations, and groups and associations at all levels of society
- Inclusion of human rights clauses in all agreements on trade or cooperation with non-EU countries
ACTIVITIES
Examine your ability to distinguish between different types of discrimination
This is a self-directed activity. The purpose of this activity is to recognize and make the difference between different forms of discrimination applied in various contexts.
Activity 1: Examine your ability to distinguish between different types of discrimination
Step 1: Read the following scenario on discrimination (racism) and answer the given question: ‘’You are in front of the classroom, and you are getting ready to enter to teach/deliver your lesson. Suddenly you see that several students are using offensive language towards an ethnic student.’’ What is your FIRST REACTION? Why?
Step 2: Now look carefully at the following contexts and forms of discrimination. Then answer the questions based on the given cartoons.
Cartoon 1

Cartoon 2

What is the level of fairness in the two cartoons?
What do you think the discriminatory context is? Why does integration fail? Do you think it has something to do with racism? Why?
What is the level of fairness in the two cartoons?
What do you think the discriminatory context is? Why does integration fail? Do you think it has something to do with racism? Why?
Activity 1: Examine your ability to distinguish between different types of discrimination
Step 3: If you had to act and change something in the two cartoons as an anti-discrimination measure, what would you do and why? Would you seek professional help or do it on your own? Note down your ideas.
ACTIVITY 2
The influences of personal experience as a first reaction in life
This is a self-directed activity. The purpose of this activity is to explore the ‘’shoes’’ of other people who have experienced discriminatory contexts and compare them with your personal experience to achieve a greater understanding of the feelings experienced.
Activity 2
- Step 1: Read the following short case studies on discrimination.
Case Study 1:
Daniel recently moved to Spain. After finding a home, he applied for several jobs. Although he met all the necessary conditions for the job, no employer called him. One day he received a phone call: he was called for an interview. He was very happy and went to the interview. After a few days, he received another phone call telling him that the job had been given to someone else. The truth was that Daniel was Roma.
Case Study 2:
‘’Sonia has been a VET teacher for more than 20 years. A vacancy for the position of the Headmaster had just been announced. After the competition and the given exams, Sonia obtained the best score among all candidates. Despite this aspect, the candidate from the second position was appointed the Director of the school. Sonia filed an appeal and the response she received was that the school needed a male Headmaster to function properly.’’
- Step 2: Think about your personal experience. Have you ever experienced a similar situation? If so, how did you proceed? If not, then how will you proceed if you experience a similar situation in the future?
ACTIVITY 3
Hate speech as a form of bridge-breaking between yourself and others
This is a self-directed activity. The purpose of this activity is to help you recognize a hate speech and shows you how it destroys the understanding between you and others by building a long-term barrier difficult to destroy.
- Step 1: Read the following headline from a famous newspaper article:
‘’Only teachers who have a personal car can teach at the school. Those who use public transportation increase the chances of transmitting flu viruses to students.’’ These words were taken from the public discourse of a well-known politician. After this speech, there was a revolt among the parents of the children enrolled in the school.
- Step 2: Now answer the following questions: Do you think this was conscious or unconscious hate speech? Why? What do you think “hurts” the most in the headline of the newspaper? How far do you think a hate speech can go?
- Step 3: Now you take on the role of a journalist. Change and reword the newspaper headline in a way that turns that hate speech into a news story that does not affect others.
ACTIVITY 3
USEFUL TIPS
- Listen to and do not judge the others based on your own personal beliefs, attitudes and biases
- Apply your skills and knowledge to avoid the “traps” of stereotyping, prejudice and discrimination
- Protect yourselves and the others against discrimination on grounds of racial or ethnic origin, religion or belief, disability, age, gender or sexual orientation
KEY TAKE AWAY
Be the change you want around you!
Take the first step towards a positive change! Discrimination only brings sadness and today’s school, and society are in crucial need of “do-gooders” people.
USEFUL READING
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND

- Let’s talk about challenging discrimination | Caring with Confidence: The Code in Action | NMC (English animation on YouTube): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gnSs0kWn8Wc
- Tackling discrimination: Council of Europe (Article): https://www.coe.int/en/web/campaign-free-to-speak-safe-to-learn/tackling-discrimination
References
Asana. (2021, May 17). 19 Unconscious Bias Examples and How to Prevent Them • Asana. Asana. https://asana.com/resources/unconscious-bias-examples
How to Really Understand Someone Else’s Point of View. (2013, April 22). Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2013/04/how-to-really-understand-someo
The Self: Meaning, Concept & Psychology | StudySmarter. (n.d.). StudySmarter US. https://www.studysmarter.us/explanations/psychology/personality-in-psychology/the-self/
Heshmat, S. (2014, December 8). Basics of Identity. Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/science-choice/201412/basics-identity
Article 21 – Non-discrimination. (2015, April 25). European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights. https://fra.europa.eu/en/eu-charter/article/21-non-discrimination#:~:text=EU%20Charter%20of%20Fundamental%20Rights
Human rights and democracy. (n.d.). European-Union.europa.eu. Retrieved January 4, 2023, from https://european-union.europa.eu/priorities-and-actions/actions-topic/human-rights-and-democracy_en#:~:text=Human%20rights%20are%20at%20the
Further Reading
Fritscher, L. (2019). Understanding Xenophobia, the Fear of Strangers. Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/xenophobia-fear-of-strangers-2671881
How to See Things from Different Points of View. (n.d.). WikiHow. https://www.wikihow.com/See-Things-from-Different-Points-of-View
Raypole, C. (2020, June 18). Sense of Self: What It Is and How to Build It. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/sense-of-self#importance
O’Keefe, A. (2020, April 9). Research Guides: Learn & Unlearn: Anti-racism Resource Guide: Conscious and Unconscious Bias. Libraryguides.saic.edu. https://libraryguides.saic.edu/learn_unlearn/foundations6
Well done! Now it’s “quiz time”! Then you can try the next module!
The European Commission’s support for the production of this publication does not constitute an endorsement of the contents, which reflect the views only of the authors, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein
project number : 2021-1-FR01-KA220-VET-



