Diversity and Tolerance in the Classroom
Diversity and Tolerance in the Classroom
This module explains the various aspects of students’ diversity, highlighting the benefits of a tolerant, diverse learning environment.
This module offers you:

INTRODUCTION
Aim & Learning Outcomes
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
Key concepts, background information, relevant theories
ACTIVITIES
Exercises, self-reflection & practical resources to promote inclusive e-learning
USEFUL TIPS
Advice, ideas and proposals on relevant issues
USEFUL READING
References and further reading
Aim
A module explaining the various aspects of learner’s diversity, highlighting the benefits of a tolerant, diverse learning environment
Learning objectives
After the completion of this module, learners (VET teachers/trainers/educators and also VET providers/Staff, as well as other key actors of educational sector) will be able to:
- Explain the concept of diversity in educational environments
- Identify and deal with challenging issues in a diverse classroom
- Acknowledge the benefits of diversity and tolerance in the classroom
At the end of this module you will know how to…
- Define diversity in learning environments
- Identify different types of diversity in classroom (internal, external, and worldview)
- Recognise barriers to learners’ participation in the educational process
- Examine strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that might arise in a diverse classroom
- Differentiate between group and individual differences in classroom
- Deal with intolerant situations that may arise during a lesson
- Share and reflect on both positive and challenging experiences of diversity in the classroom
- Explore the benefits of a tolerant, diverse classroom for all learners
- Work with others, in particular their learners, to promote diversity and tolerance in learning environments
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND

This module is combined of three units:
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Intersectionality
- Teaching Tolerance
Unit 2.1: Diversity & Inclusion
What is Diversity ?

- Diversity is inclusive of all forms of social difference between people including race, gender, sexuality, (dis)ability, ethnicity, nationality, social class, political persuasion, and age.
- Diversity in a learning environment can take many different forms.
- It is important to acknowledge the range of differences that exist in the classroom so all learners are included.
Unit 2.1: Diversity & Inclusion
- Classrooms are very diverse places. Every child has a different background and experiences that make them their own individual person.
- Therefore, it is important that all experiences and ways of being are handled with fairness and justice.
- Diversity in the classroom can take many different forms. Not every form of diversity is obvious to the naked eye, as shown below. Not every learner will be visibly diverse from one another, but that does not make them any less prone to discrimination or unfair treatment.

Ahmed is Muslim

Michael has two dads

Anna is mixed race

Conor’s parents cannot afford much

Lucy has a learning disability

Ellie is from an ethnic minority

Paul comes from a different country

Susie has epilepsy
Unit 2.1: Different Types of Diversity
Internal diversity refers to characteristics which people are born with such as race, ethnicity, sexuality, gender, nationality, and (dis)ability.
External diversity refers to characteristics that significantly influence a person’s life such as religion, social class, and citizenship.
Global diversity refers to the characteristics that can change with time as we begin to conceptualise the world differently, such as political beliefs and education.
Unit 2.1: Supporting Diversity

- Learning how to support differences in the classroom can help to transform the way that learners think, learn, and act.
- Supporting diversity in the classroom is very important. Not only does it help to build social awareness in learners, but it also helps every learner to feel represented and included.
- In a diverse classroom, students learn to work with and appreciate individuals from different backgrounds, which can better prepare them for the real world where they will interact with people from diverse backgrounds.
- Diversity in the classroom also encourages better academic results as it improves critical thinking amongst learners (Kampen, 2020).
Unit 2.1: Celebrating Diversity in the Classroom
There are many ways you can promote diversity in the classroom, for example:
- Use diverse learning and teaching materials that represent different viewpoints and perspectives.
- Encourage and support students to share differing viewpoints to increase participation and teach them to work together.
- Get to know your students beyond just their name, including their background, culture, and important issues to them and their families.
- Connect with families and community leaders to reflect and celebrate diversity within the community.
- Celebrate diversity by allowing students to share their diverse stories with classmates and honor their differences.
Unit 2.1: Benefits of Diversity in the Classroom

One way to support and encourage inclusion in a diverse classroom is by teaching learners about intersectionality…
- Learners are given the opportunity to learn from each other’s perspectives and upbringings.
- Having diverse representation in the classroom promotes feelings of self-worth amongst all learners.
- Learners improve their problem-solving skills when working in diverse groups.
- Increased diversity in education helps to reduce prejudice among learners and parents.
Unit 2.2: Intersectionality
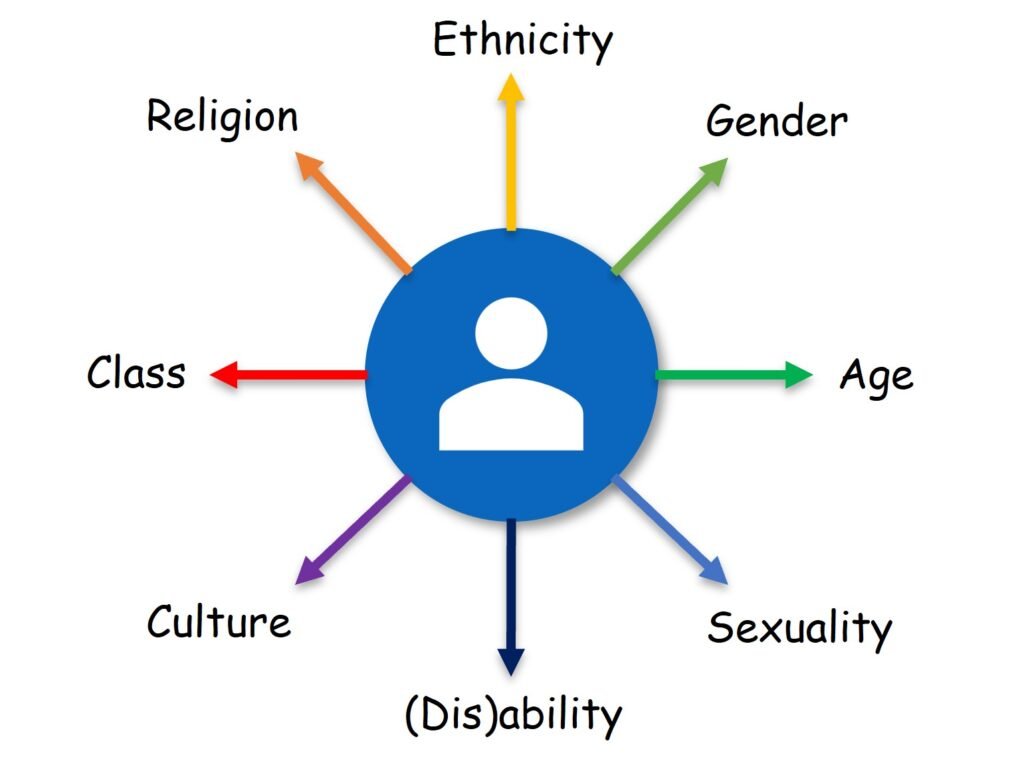
- Intersectionality is the combination of different identities that make up a whole person.
- By teaching learners about intersectionality, trainers can encourage open conversations and deeper understanding between children.
- Activities that explore the different components that make up each learner can help learners to understand the similarities and differences between each person.
Unit 2.2: Intersectionality in the Classroom
- In a single classroom, there can be many shared group characteristics, as well as individual characteristics.
- The most common shared group characteristics include: race, ethnicity, religion, gender, age, and nationality.
- However, more individualised characteristics can include things such as physical ability, sexuality, and social class.
- While it is important to highlight and celebrate individuality to promote tolerance, it is also important to recognise that not every child will be comfortable sharing their diverse experiences.
- Educators should work with learners to create projects and activities where every learner has the opportunity to share about and celebrate themselves.
Unit 2.2: An Intersectional Approach

- An intersectional approach to diversity in education recognises that individuals have multiple identities and experiences that can impact their access to education, success, and well-being. By addressing the unique needs of marginalised groups, institutions can create more inclusive environments where all students feel supported. This approach also helps to challenge systemic inequalities by recognising how different forms of discrimination intersect and compound one another, impacting the experiences of marginalised students.
Unit 2.2: Social Inclusion
Intersectionality can help to improve the social inclusion of all groups. Here are some examples of ways that incorporating intersectionality into the classroom can help improve social inclusion for all…
Acknowledging and valuing diversity –
- It recognises that each individual has a unique set of social identities (such as race, gender, sexual orientation, religion, ability, etc.) that intersect and shape their experiences
- By acknowledging and valuing this diversity, teachers can create a classroom environment that respects and celebrates different identities and experiences.
Addressing biases and stereotypes –
- This involves critically examining biases and stereotypes that may exist within the classroom and the broader society.
- Teachers can help students understand how these biases and stereotypes can lead to exclusion and discrimination, and encourage them to challenge these harmful beliefs.
Incorporating diverse perspectives and experiences –
- This can include teaching about the contributions of marginalised groups to history and society, using inclusive language and imagery in textbooks and other learning materials, and creating opportunities for students to share their own experiences and perspectives.
Creating a safe and inclusive learning environment –
- This can involve implementing inclusive classroom policies and practices, such as using gender-neutral language, respecting students’ pronouns, and providing accommodations for students with disabilities.
Unit 2.2: Barriers to Learner Participation
- Some learners who may experience social exclusion from their peers because of social class or disability and so they may find it difficult to participate in such activities.
- This can be very challenging for educators who do not wish to exclude these learners but also may find it difficult to plan activities or lessons that are fully inclusive of these learners.
- Below are some resources that you can use to help you plan inclusive lessons and activities for all learners…
Unit 2.3: The Importance of Tolerance
- The aim of promoting and encouraging inclusivity for all people in the classroom is social tolerance.
- By integrating diversity into lessons and activities from an early age, learners are more likely to be respectful, tolerant, and inclusive of other people.
- Simple things such as using diverse learning materials, promoting inclusivity by displaying educational posters around the room, and fostering open conversations are all great ways to encourage inclusivity in the classroom.
Unit 2.3: The Importance of Tolerance
- Teaching tolerance to students in diverse classrooms is crucial for creating a safe and inclusive learning environment where all students feel respected and valued.
- When students are taught to be tolerant, they learn to appreciate and accept the differences between themselves and their peers, which can help to prevent bullying, discrimination, and exclusion.
- Tolerance prepares students for life beyond the classroom – where they will encounter people from different backgrounds and cultures. It is essential for students to develop the skills and attitudes necessary to navigate diverse social environments.
Unit 2.3: Fostering Tolerance
One of the best ways that educators can encourage tolerance in the classroom is by giving learners different social experiences.
Here are some ways that educators can integrate social awareness in the classroom…
Set up a map where learners can complete projects about different countries and cultures across the world that is visible in the classroom
Give learners the opportunity to bring in foods from different cultures/religions, etc. so learners can experience different foods and treats
Encourage learners to learn a few basic phrases from the languages that can be found in the classroom
Take some time to educate learners about the different types of disability and how it affects a person’s life and learning
Make sure to celebrate different religious holy days, cultural days, or any other special day equally. Give learners opportunities to share their own cultures
Make sure the classroom library is diverse as possible – books should have protagonist of all races, cultures, religions, sexuality, and physical ability
ACTIVITIES
Diversity SWOT
The purpose of this activity is to understand and identify the difference strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that could potentially arise in a diverse classroom.
Activity 1: SWOT Analysis
STRENGTHS
1.
2.
3.
WEAKNESSES
1.
2.
3.
OPPORTUNITIES
1.
2.
3.
THREATS
1.
2.
3.
Time: 30 minutes
Instructions:
1.For 5 minutes, reflect on the diversity that can be found in your current classroom of learners.
2.For the next 20 minutes, consider the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a diverse classroom to teaching.
3.Once the SWOT analysis has been completed, take the final 5 minutes to reflect on what you have written with the following questions:
❑Was it easier to identify strengths/opportunities than weaknesses/threats to diversity in your classroom?
❑What was the main strength/weakness of diversity in the classroom? Why?
ACTIVITY 2 Dealing with Moments of Intolerance
Dealing with Moments of Intolerance
- The purpose of this activity is to encourage educators to examine and confront scenarios of intolerance in the classroom between learners by creating specific lesson plans aimed at educating about different scenarios.
Activity 2: Dealing with Moments of Intolerance

Time: 60 minutes
You will be brought through a series of scenarios where you will be prompted to consider what actions you will take to resolve the situation between learners.
These scenarios are aimed to showcase the different types of intolerance that can intentionally or unintentionally occur in a classroom, and are generated to prompt creative and culturally aware problem-solving activities.
To complete this activity, you should complete a small lesson plan containing 1x video, 1x activity, and 1x group discussion to prompt conversation between the learners about diversity and tolerance.
Paul has recently moved to your country after fleeing his home country because of war. Paul has a very limited grasp on the language and struggles with how quickly everybody speaks to him. Recently you have noticed that the other learners have stopped trying to include Paul altogether during class time.
You have asked another learner Amy to understand why. Amy has told you that the other learners don’t like talking to Paul because he doesn’t understand and he cannot speak properly. She also confessed that some of the other learners say that Paul overreacts to certain situations sometimes, and many of the other learners find this to be very off-putting. Paul has Asperger’s Syndrome.
You are tasked with creating a 45 minute lesson plan that aims to educate the other learners about Paul’s developmental disability as well as his culture.
Somaya is the only learner of Arabic origin in your classroom. Somaya was born in your country and is a practicing Muslim. She has decided this year that she would like to start wearing the hijab and recently started wearing it to your vocational college. You have noticed that the other girls are making fun of Somaya for her hijab, and that one girl in particular has tried to pull Somaya’s hijab off.
One of the boys in your class has confessed to you that the boys have started calling Somaya names, and that they are excluding her from all activities. Somaya has mentioned to you that she would like to talk about Islam to her peers so that they understand her choice to wear the hijab now.
You are tasked with creating a 45 minute lesson plan that educates the other VET learners about Somaya’s religion.
George, Miguel, and Isla are best friends. The three are inseparable and do everything together. However recently you have begun to notice that George and Miguel are excluding Isla at breaktimes, and no longer talk to her during class. Isla has begun to spend her lunch time on her own inside, while Miguel and George are going to the canteen to have their lunch as usual. The other day you asked Isla why she was not going to the restaurant with the boys, and she broke down in tears and ran away.
Very concerned, you ring Isla’s mother, who informs you that she has just lost her job and can no longer afford to give Isla her allowance which helps to supplement her meals in college.
You are tasked with creating a 45 minute lesson plan that aims to educate your learners about social awareness around money.
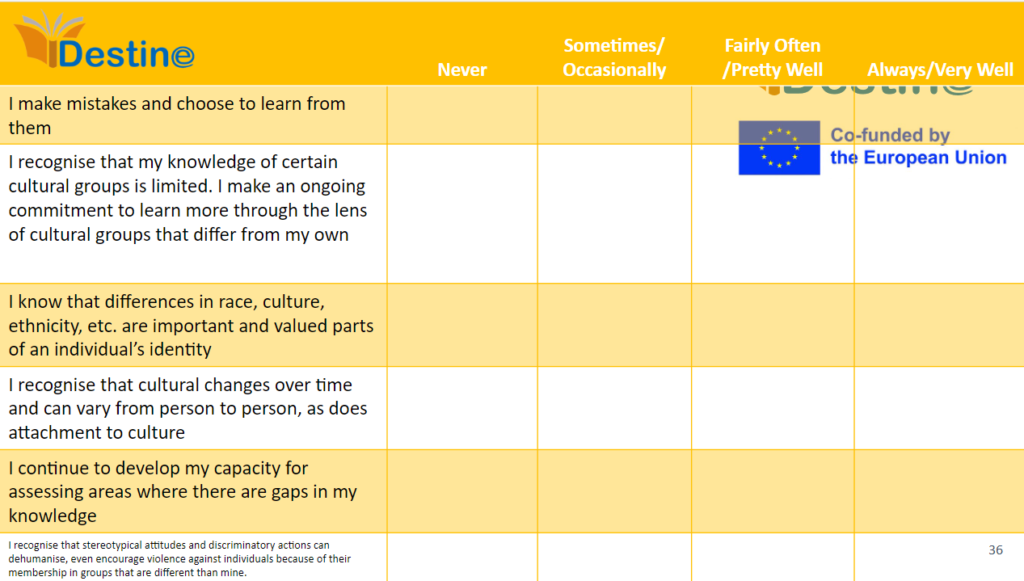
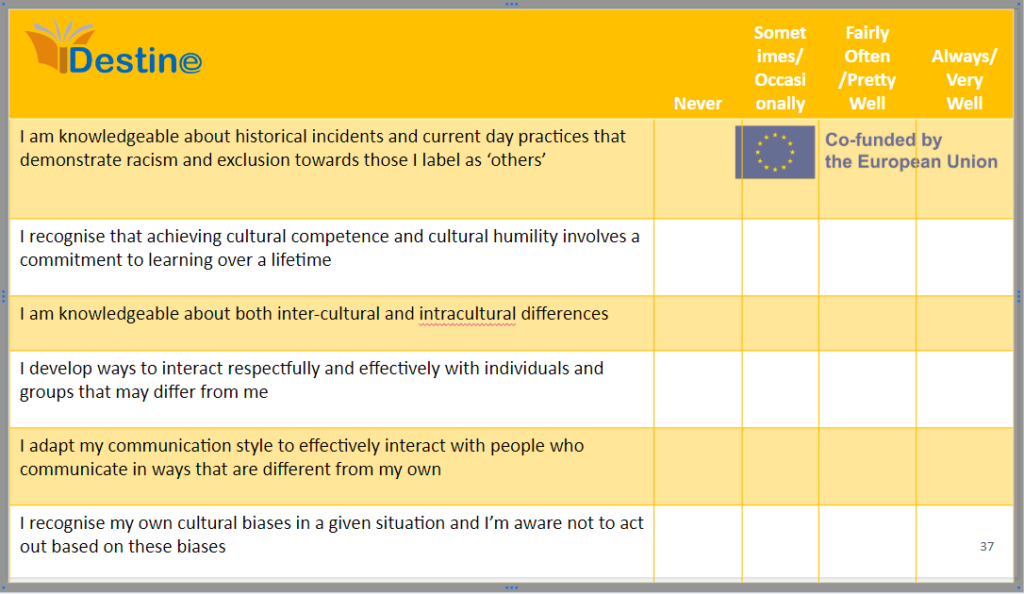
ACTIVITY 3 Cultural Diversity Self-Assessment Survey
Cultural Diversity Self-Assessment Survey
Brief introduction to this activity or resource that addresses the VET educators themselves (e.g. self-reflection or self directed exercise) or is an activity that will be implemented by a trainers’ trainer
Activity 3: Cultural Diversity Awareness Survey
- Take the next 15 minutes to complete the cultural diversity awareness survey by yourself.
- The aim of this survey is to teach you about your own subconscious biases. Answer the questions as honestly as possible.
- Once you complete the quiz, take 10 minutes to evaluate how many times you answered ‘Never’ or ‘Sometimes/Occasionally’, and think of the ways you will try to improve these areas going forward.
Remember! Everybody suffers from cultural bias and this survey is not meant to shame participants, only to educate you on areas for improvement.
USEFUL TIPS

- Make sure not to single out specific learners and instead educate the entire class.
- Use teaching materials that represent different viewpoints, perspectives, and experiences.
- Celebrate and appreciate differences among students and address any instances of discrimination or bias.
- Incorporate texts and media that include characters from diverse backgrounds and cultures and expose students to different languages and customs.
- Encourage open and respectful dialogue among students and ensure that all voices are heard and respected.

- Create an environment where students feel comfortable sharing their opinions and perspectives.
- Model inclusive behaviour by treating all students with respect and valuing diversity in the classroom.
- Celebrate diversity by incorporating holidays and events from different cultures and backgrounds into the classroom.
- Encourage students to share their diverse experiences and stories with classmates and create a space where all students feel valued and included.
KEY TAKE-AWAYS
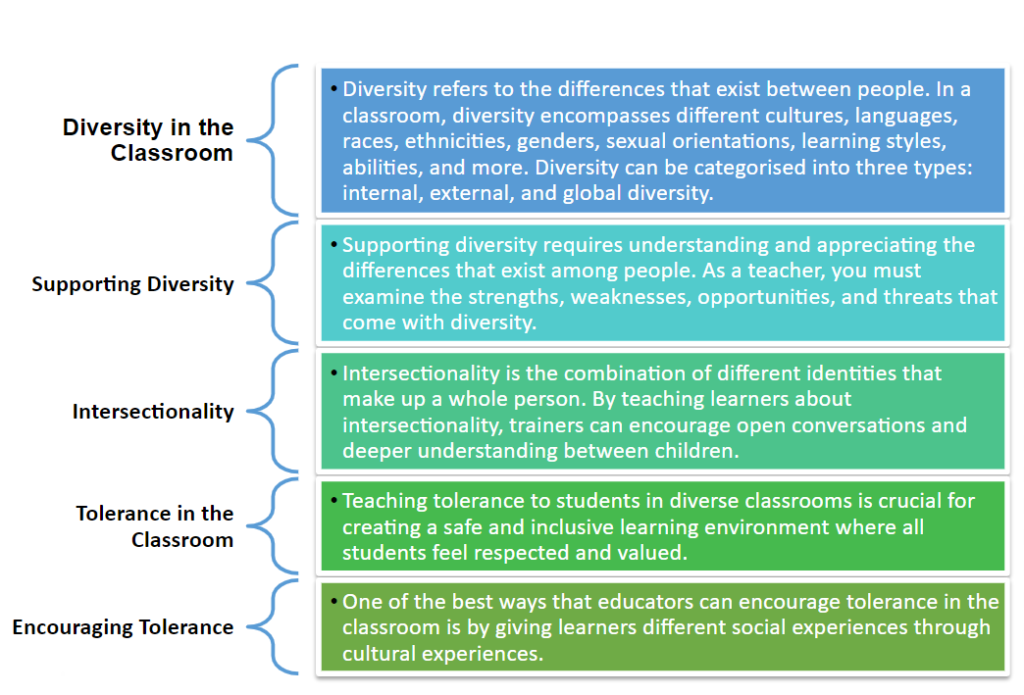
5 Keys to Tolerant Teaching
Well done! Now it’s “quiz time”! Then you can try the next module!
The European Commission’s support for the production of this publication does not constitute an endorsement of the contents, which reflect the views only of the authors, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein
Project number : 2021-1-FR01-KA220-VET-