
Using digital tools to engage in learning and assess the results
Using digital tools to engage in learning and assess the results
This module presents strategies how to engage students and assess online courses, helping educators critically reflect on evaluation processes in a diverse learning environment.
This module offers you:

INTRODUCTION
Aim & Learning Outcomes
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
Key concepts, background information, relevant theories
ACTIVITIES
Exercises, self-reflection & practical resources to promote inclusive e-learning
USEFUL TIPS
Advice, ideas and proposals on relevant issues
USEFUL READING
References and further reading
Aim
A module exploring strategies how to engage students and assess online courses, helping educators critically reflect on evaluation processes in a diverse learning environment
Learning objectives
After the completion of this module, learners (VET teachers/trainers/educators and also VET providers/Staff, as well as other key actors of educational sector) will be able to:
- Understand the importance of varied engagement and evaluation methods
- Create engaging online lessons
- Evaluate the effects that diversity and digital technology have on data that is used to evaluate educational performance
At the end of this module you will know how to…
- Discuss definitions of student engagement and evaluation
- Define different kinds of data used in performance evaluation (quantitative vs. qualitative)
- Understand the way that extra-scholastic circumstances may affect the academic performance of students
- Choose evaluation strategies and digital tools that enhance students’ online participation and promote teamwork
- Identify forms of examination fit to educational purpose in a learning environment
- Be able to apply at least 2-3 different evaluation techniques in an online learning environment
- Reflect on personal, engaging learning experiences
- Choose between different kinds of evaluation in order to mitigate the negative effects digital environments may have on student motivation/participation or external variables such as socio-economic class or difficult family/community situations
- Design and develop fair evaluations that more accurately measure academic performance while controlling for external influences
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND

This modules demonstrates the benefits of three different units:
- Student Engagement and Evaluation
- Circumstances that may affect students’ academic performance
- Data used in performance evaluation
Unit 7.1: Student Engagement and Evaluation
- Student engagement is a term that has risen in popularity during recent decades and is predicated on the belief that learning improves when students are active in and out of the classroom. (Major,2020)
- Engagement is more complex than asking and answering questions. We can understand more about student participation through the three dimensions of a person’s attitude: Cognitive, Affective and Behavioral (Major, 2020 and Foster,2022).
- It is important to understand that engagement is not stable overtime and that it varies from student to student.
- In the table below you can see and identify the signs that correspond to engagement in the classroom in each one of the three dimensions (Foster,2022):

- Student participation is a primary assessment indicator for engagement. However, engagement is more complex than that. Designing reflective and thoughtful assessments of engagement that tap into the cognitive, behavioral and affective dimensions will help the teacher effectively evaluate the student’s active learning experience in their class and improve drastically their lesson. (Lang,2021)
- By understanding the different factors that may affect student engagement in the e-classroom, and take student’s feedback into consideration, the classroom immediately becomes more inclusive and accepting of difference.
Unit 7.2: Circumstances that may affect students’ academic performance
- Socio –Economic Factors: Age, Family Support, Residence proximity to school, self-motivation, involvement in class activities, self-confidence, absenteeism, race, disability, gender
- Parental Background Factors: Educational status, Parental Income, Household Size
- Peer Related Factors: Peer Support, Peers with Academic Background
Teaching inclusively means embracing student diversity in all forms – race, ethnicity, gender, disability, socioeconomic background, ideology, and personality traits like introversion. It means designing and teaching courses in ways that foster talent in all students, but especially those who come from groups traditionally excluded in education.
Unit 7.3: Data used in performance evaluation
Assessments may differ from the traditional classroom to the e-classroom. Keeping students engaged during an online course content is more challenging than keeping them engaged in the traditional classroom. Apart from including data related to their understanding of the course content you could also collect data to assess students engagement and participation (Lang,2021):
- Quantitative Data to be collected during the lesson will mostly assess student participation:
- Students’ attendance
- Number of questions asked during the lesson
- Time spent with students having an active discussion on the subject during class
- Number of students that prepared materials before the lesson
- Number of students that completed activities, projects, and assessments after the class
Unit 7.3: Data used in performance evaluation
2. The Qualitative Data will mostly assess students’ engagement and active learning. Applying the three dimensions of a person’s attitude into the assessment you should look for the following data (Foster,2022) :

Unit 7.4: Types of Online Assessments
- Use technology to help kids get to know you and one another.
- Use a poll on your video conferencing system or another digital tool to elicit data from students in order to develop learning objectives or goals.
- Encourage students to recognise course guidelines by having them take a quiz on the curriculum.
- Use an online treasure hunt to get students interested in previewing the content.
- Give learners a form to fill out while they read or view the content
- After a section of information, provide a low-risk or ungraded exam to enable the students review key ideas or abilities (Cook & Babon, 2017)
- Use question-and-answer formats in interactive video programs like EdPuzzle.
- Make interactive games and puzzles, such as the free, open-source Materia widgets, to offer fun possibilities for practice and review.
By including evaluation criteria (such as a rubric) at the start of an assignment or assessment, instructors may encourage students to analyze and edit their own work before turning it in for marking. This is a fantastic technique to assist learners in assessing their work critically and making improvements to it in order to progress their learning and performance. Instead of focusing on the obvious, evaluation criteria should evaluate the most crucial, significant components of students’ work (Major,2020).
Encourage students to look beyond description to unearth a tale of a situation or application from their own points of view in order to engage them in reflection that leads to reflexivity (marked by an outcome or change in behavior). Tasks and interpersonal interactions cause reflexivity (Kahn, Everington, Kelm, et al., 2017). Ask a series of questions or provide a number of guided suggestions so that students may reflect on their own feelings, experiences, actions, and thoughts in connection to an educational component. Encourage students to use a range of internet resources, including videos, blogs, discussion forums, or or Sutori timelines, to collect their own personal tales or offer their viewpoints (Major,2020).
Encourage students to produce a paper or deliver a speech for a live audience or for later watching in order to evaluate how they interpret the course material (Major,2020). Think about the following concepts for inventive written or spoken assessments:
- Send in a one-minute essay or recording
- Use VoiceThread, for example, to respond to a case-based (case study or video) assignment.
- Create a bibliography with annotations.
- Review of creative materials related to the content (a book, play, article, video, artwork, or performance)
- Make an executive summary or briefing.
- Using Canva or Adobe Spark, create charts, graphs, or visual journalism.
Real-world or situational contexts where the knowledge may be applied or evoked are the focus of authentic assignments, which challenge students to produce creative work. These tasks are frequently student-centered and demand for the production of a generative deliverable, the demonstration of mastery through the application, the gathering of special resources, or the synthesis of important skills. Usually, a deliverable in the form of an uploaded document, video, or commentary serves as evidence (McGuire, S., & Angelo, T., 2015). A few instances of authentic evaluations are:
- Reflections on one’s own real-world applications or experiences
- Assignments based on projects
- To find positive learning experiences for generative action, use appreciative pedagogy
- Service-learning activities or projects
- Portfolio development
Selected-response test items (to include matching, true-false, or multiple-choice items) are frequently classified by the depth of knowledge required to address them, such as:
- Recall of facts or procedures by asking students to recognize definitions, facts or procedures
- Understanding of concepts or skills by asking students to review some information and reach a conclusion such as a diagnosis, cause or effect.
- Strategic thinking to solve a problem by asking students to actively solve a problem with the knowledge they have acquired
Put one or more students together to give them a collective, interactive way to show what they have learned. This can be done through social media with a specific hashtag, video conferencing, collaborative papers or platforms, or exchanges via video recordings, discussion forums, or other online platforms. Indicate whether groups or individuals will earn a mark for each assignment.
Here are some suggestions for group evaluations:
- Use “Socratic Questions” as discussion starters
- Peer assessment of their assignments prior to their due date
- Collaborative Interactions through digital tools such as Padlet to stimulate problem solving and critical thinking
- Activities where students may engage in conversation with other students that make up their audience:
After you’ve completed a section of the lesson, ask students to reply to questions similar to “What was the most essential part of the lesson so far?”, ” What still remains unanswered regarding the covered material?”.
Students are frequently asked to explain their learning in summarizing evaluations. These exercises take place at the completion of a module or course. Examples include:
- Utilize digital tools like Padlet to create sections where students can collectively gather their learning.
- See more examples in activity section
DIGITAL TOOLS

- Wordwall is an online application having custom activities for online classrooms
- It has many templates that can be easily created and used
- The learners receive feedback while they are doing the activity. No need for instructors’ feedback
- Each activity can be embedded on the MOOC Platform
- Each activity can also be printable

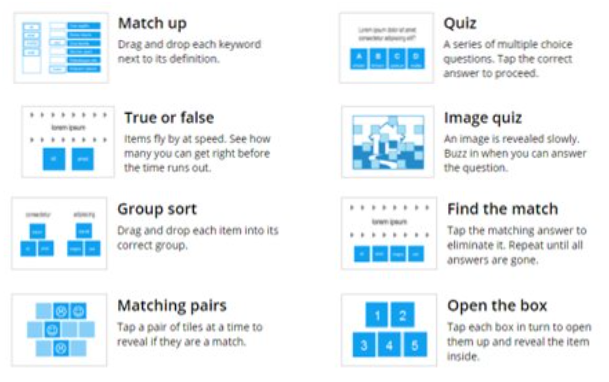

Types of Activities and Functions

Classic Function

Students watch the video individually
They work independently and at their own pace
Perfect for rotation stations or flipped classroom
Live mode

You project the video in front of the class
Students answer on their own devices in real time
You get live feedback to spark in-class discussion
Classic Class

Students need to log in or sign up
Track students’ progress across all videos
Open Class

Students don’t need an account
See students’ progress one video at a time
Perfect for demos, quick practice

- Edpuzzle is an online educational application for creating or editing video lesson
- You can record a video and use voice over
- The learners watch a video and answer pop-up questions (3 types of questions)
- Edpuzzle LMS integration
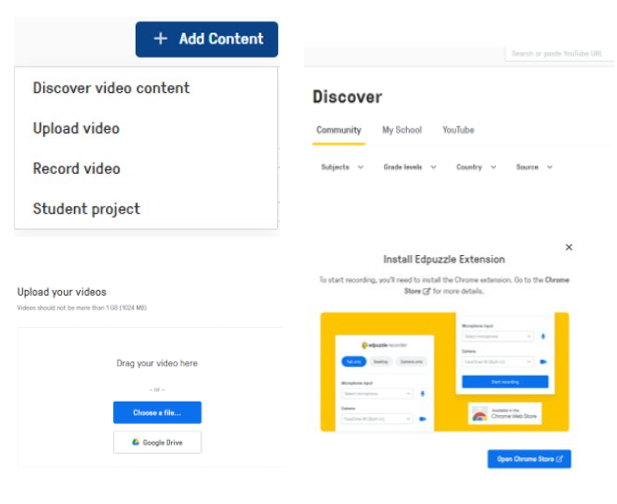
Moodle Integration - Using Edpuzzle with Moodle

Visit this link to watch the tutorials on how to integrate EdPuzzle to your Mooc Platform and how to assign a video lesson on moodle.

- Quizlet is a web-based application developed to help learners study information through interactive tools and games.
- It is very useful for creating a glossary and assessments
- Quizlet has sets. You create a set of words (terms and definition with pictures)
FLASHCARDS
The students study the terms and definitions.

LEARN
The students can practice the terms with this feature.

TEST
The students can test their knowledge.
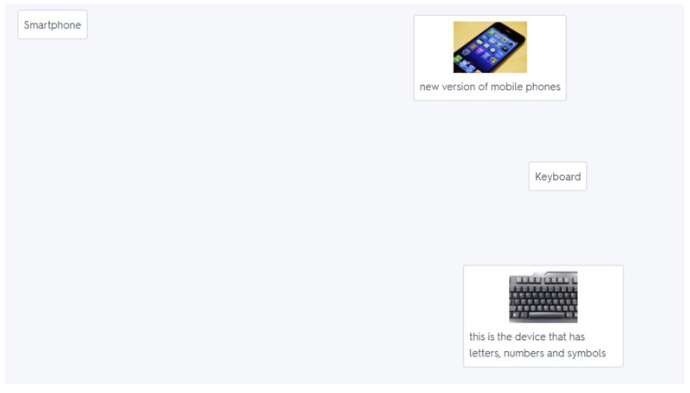
MATCH
Assessment : The learners connect the term with the definition.

- Padlet is a canvas to create beautiful projects that are easy to share and collaborate on.
- It works like a piece of paper. They give you an empty page – a padlet – and you can put whatever you like on it.
- Drag in a video, record an interview, snap a selfie, write your own text posts or upload some documents, and voilà! A padlet is born. Make it even more beautiful by choosing custom wallpapers and themes.
You can use different type of board layouts according to the needs of the activity you want to do.
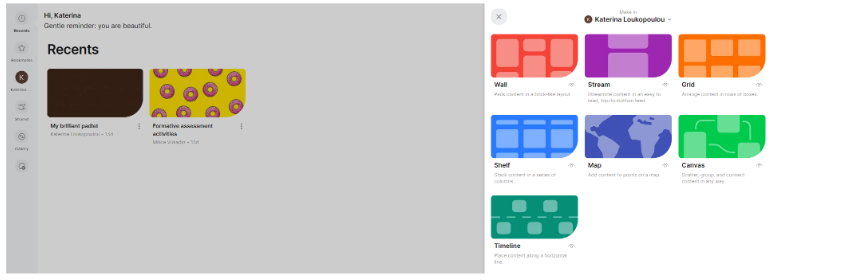
You can modify each board by utilizing one of these pictures.
You can post images, make polls, record audio, ask students to contribute to the board and many many other activities!
Think of padlet as an extension of the classic whiteboard that can include articles, images, videos, drawings etc.

ACTIVITIES
ACTIVITY 1
Develop an evaluation activity choosing a specific method and digital application.
This is self-directed exercise for the learner to combine theoretical knowledge with the right digital application.
Choose an engaging evaluation methodology ( Introductory Assessment, During or after content engagement, Self-Assessment, Reflexivity in Assessment, Writing or Oral Assessment, Authentic Assessment, Selected-Response Assessment , Group Assessment, Summarizing Assessment
Prepare the content you want to evaluate students on
Decide on the appropriate Digital Application ( Wordwall, EdPuzzle, Quizlet, Padlet)
Decide on which Activity you will use ( Flashcards, Quiz, Match etc.)
Adapt the content to the activity you chose
Share the activity with the students
Test the activity
ACTIVITY 2
Match the Assessment with the Assessment Type.
This is self-reflection activity on the different engaging evaluation methods you may use in an e-learning environment.
- Visit this link and match each assessment type with the correct assessment.
- After you are done click submit and cross check your answers!
USEFUL TIPS
Useful Tips!
- Choose the Right Digital Tool: There are many digital applications available for creating assessments, such as Google Forms, Kahoot, Quizlet, and many more. Select the one that best suits your needs and goals.
- Keep it Simple: When designing assessments, it’s important to keep the format simple and easy to follow. Make sure the questions are clear and concise.
- Mix it Up: Use a variety of question formats, such as multiple-choice, true/false, short-answer, and matching. This keeps the assessment interesting and engaging for the students.
- Use Visuals: Incorporate images, videos, and other multimedia to make the assessment more engaging and interactive.
- Use Gamification Techniques: Gamification can be a powerful way to increase engagement in assessments. Use tools like badges, leaderboards, and progress bars to motivate students.
- Provide Feedback: Make sure to provide immediate feedback after each question. This helps students learn from their mistakes and reinforces their understanding of the material.
- Test the Assessment: Before administering the assessment, test it out to make sure it’s functioning properly and all the questions are clear
KEY TAKE AWAY
Remember!
- Student Participation does not equal Student Engagement.
- There multiple socioeconomic factors that may affect students academic performance.
- Engaging Evaluation methods and activities will help make your classroom more inclusive.
- There 8 different types of evaluation you can use in the online and the traditional classroom.
- Main digital tools for online students engagement are: Wordwall, EdPuzzle, Quizlet and Padlet.
- Wordwall and Quizlet may be integrated into the Mooc Platform.
USEFUL READING
- Major, A. E. E. (2020, October 26). Keeping Students Engaged: How to Rethink Your Assessments Amidst the Shift to Online Learning. Faculty Focus | Higher Ed Teaching & Learning. https://www.facultyfocus.com/articles/educational-assessment/keeping-students-engaged-how-to-rethink-your-assessments-amidst-the-shift-to-online-learning/
- Foster, S. (2022, September 7). Facilitating and assessing student engagement in the classroom. Center for Teaching & Learning. https://www.colorado.edu/center/teaching-learning/2022/03/03/facilitating-and-assessing-student-engagement-classroom
- McGuire, S. Y., McGuire, S., & Angelo, T. (2015). Teach Students How to Learn: Strategies You Can Incorporate Into Any Course to Improve Student Metacognition, Study Skills, and Motivation (1st ed.). Stylus Publishing.
- https://el.padlet.com/dashboard
- https://wordwall.net/myactivities
- https://quizlet.com/
- https://edpuzzle.com/
- https://www.inclusiveeducators.eu/good-practice-compendium-for-creative-classrooms/
Well done! Now it’s “quiz time”! Then you can try the next module!
The European Commission’s support for the production of this publication does not constitute an endorsement of the contents, which reflect the views only of the authors, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein
project number : 2021-1-FR01-KA220-VET-

